Featured
Voltage Across Capacitor Circuits
Voltage Across Capacitor Circuits. Due to the application of alternating voltage across the capacitor the electrons move to and fro around the circuit, thus constituting alternating current. Therefore the energy stored in the capacitors is:
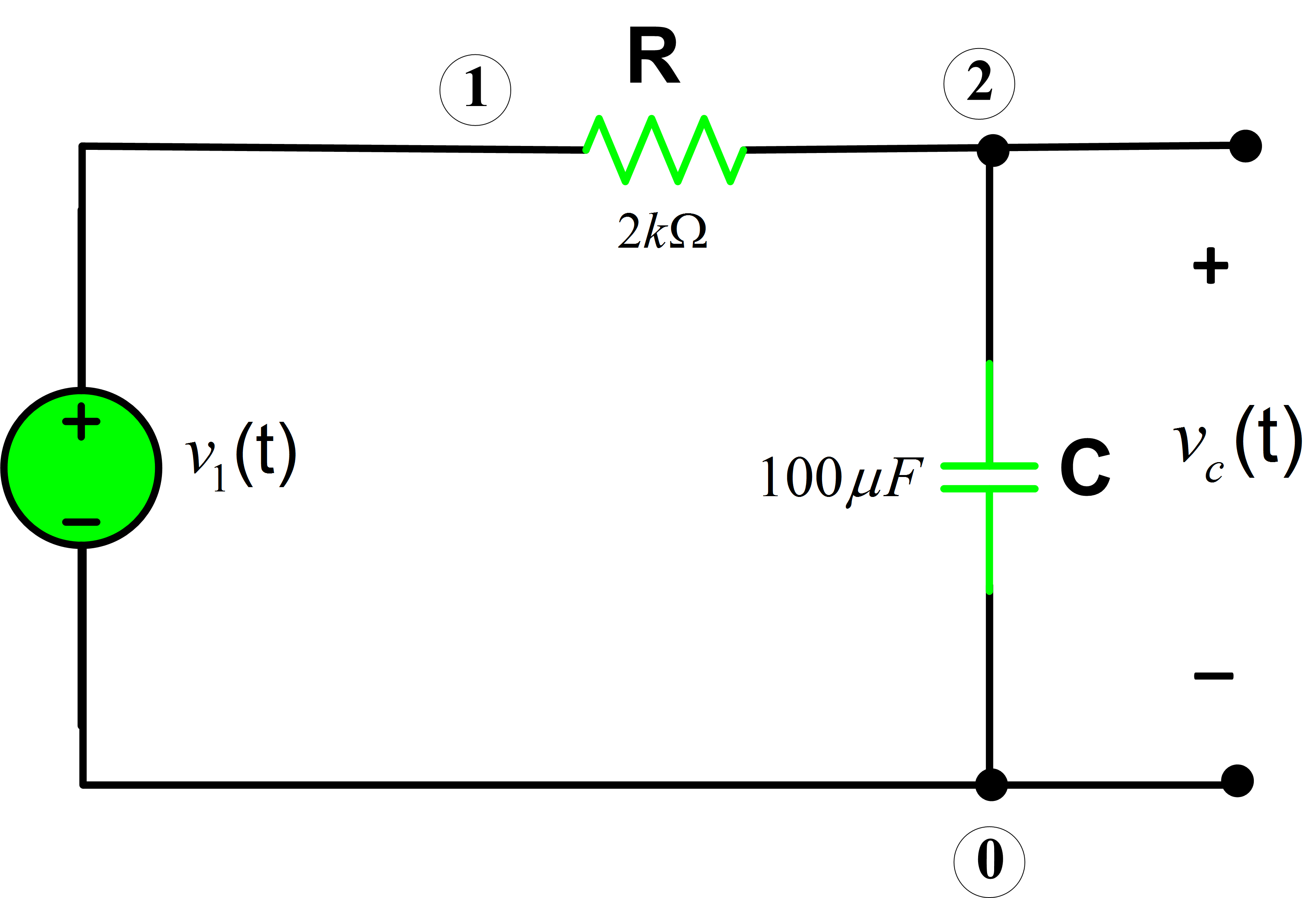
As to the other circuit you have presented use the kirchoff voltage law Due to the application of alternating voltage across the capacitor the electrons move to and fro around the circuit, thus constituting alternating current. If the voltage across the capacitor is defined as the output signal of the circuit, the transfer function is h (s) = vo/v = (1/sc)/ (r+sl+1/sc)=1/ (s^2lc+rcs+1).
The Series Circuit Has An Impedance:
Capacitor voltage lags capacitor current by 90°. If we were to plot the current and voltage for this very simple circuit, it would look something like this: In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each capacitor is the same and equal to the total voltage in the circuit.
Example For Series Capacitor Circuit:
Then 8.16 + 3.84 = 12v. Since kirchhoff’s voltage law applies to this and every series connected circuit, the total sum of the individual voltage drops will be equal in value to the supply voltage, vs. So whatever is the voltage ouput of pin 3 of the 7400 only half goes to c28.
262 3 11 3 10 10 10 500Μjoules C 22 Ec==V×− ×=
C1 = 470nf and c2 = 1μf. If the voltage across the capacitor is defined as the output signal of the circuit, the transfer function is h (s) = vo/v = (1/sc)/ (r+sl+1/sc)=1/ (s^2lc+rcs+1). Consider a series lcr circuit with an a.c.
We Also See From The Above Equations That The Current In A Capacitive Circuit Is Π/2 Ahead Of The Voltage Across The Capacitor.
T is the elapsed time since the application of the supply voltage; Now, in the below example we will show you how to calculate total capacitance and individual rms voltage drop across each capacitor. In short, the working voltage of a capacitor in a dc circuit is named wvdc.
In Typical Discussion Of Ac Voltage, We Refer To The Rms Voltage.
Only the resistor r resists the maximum current flow through the circuit. For an uncharged capacitor, the current through the circuit will be maximum at the instant of switching. Suppose if the circuit consists of more than one capacitor in the circuit.
Comments
Post a Comment