Featured
Power Equation With Voltage And Current
Power Equation With Voltage And Current. You can check this by dividing 432 watts by 108 watts and seeing that the ratio between them is indeed 4. In regard to voltage and resistance, it is articulated as \(p = \frac{v^{2}}{r}\) where, a voltage applied across the two ends =v,
Z h = impedance at h th harmonic. I = electric current passing through the circuit. One ohm is defined as the resistance which allows the current of one ampere under a.
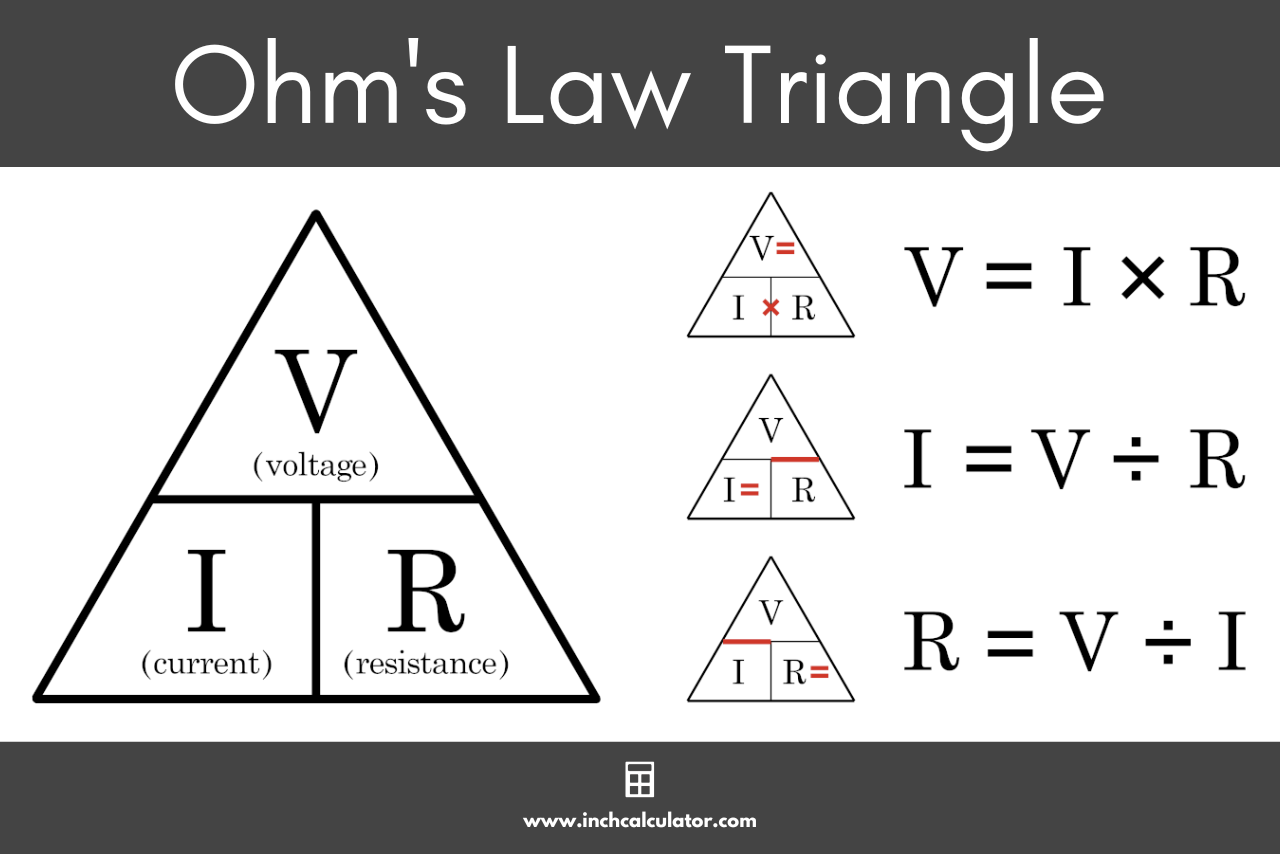
From Ohm's Law We Know That Voltage Is The Product Between Current And Electric Resistance.
I = √p/r (4) electrical resistance formulas. (2) electrical potential or voltage formula in dc circuits. If there is ac, look also at the power factor pf = cos φ and φ = power factor angle
For Example, If You Have A Power Of 10W With A Current Of 2A The Voltage Is 10W / 2A = 5V.
In any electrical circuit, the power is computed making use of these three formulas. Combining the above equations give the pv cell (module) characteristic equation: \[ i = \frac{u}{r} \tag{7} \] replacing equations (6) in (4), gives the formula for electric power as:
One Ohm Is Defined As The Resistance Which Allows The Current Of One Ampere Under A.
We use a power factor formula to calculate the power in a circuit with active voltage and current within a certain time. I = current in amperes (a) v = voltage in volts (v) p = power in watts (w) r = resistance in ohm (ω) V = p / i;
A Current Of 5 A Flows Through An Electric Heater When It Is Connected To A 240 V Mains Supply.
I = current in amperes (a) v = voltage in volts (v) p = power in watts (w) r = resistance in ohm (ω) z = impedance = resistance of ac circuits in ohms; P = v 2 r. The characteristic equations can be used for find both the output voltage and current.
V = √ (P X R) (3) Electrical Current Formulas In Dc Circuit.
P = √3 × pf × i × v where pf is the power factor, i is the current, v is the voltage and p is the power. The current through the diode is given by shockley's equation: Power p = i × v = r × i 2 = v 2 ⁄ r where power p is in watts, voltage v is in volts and current i is in amperes (dc).
Comments
Post a Comment